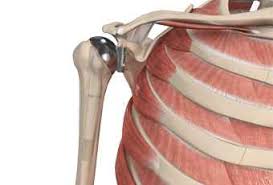
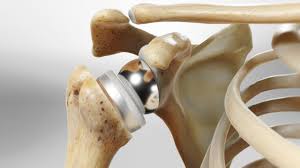
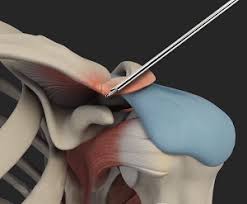
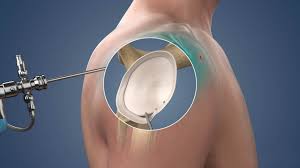
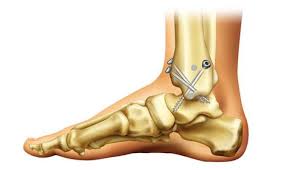
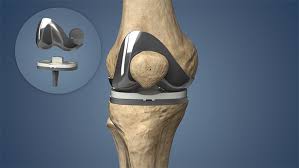
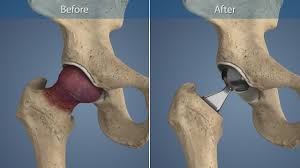
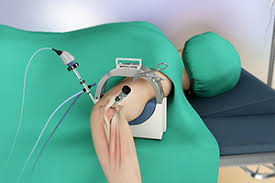
Primary Knee replacement
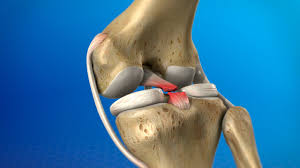
Primary knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at alleviating pain and restoring function in individuals suffering from severe knee conditions, primarily osteoarthritis. This procedure involves the removal of damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components. Over the years, knee replacements have become increasingly common, providing significant relief to patients who have exhausted non-surgical treatment options.
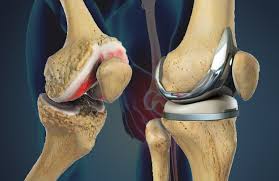
The primary indication for knee replacement surgery is advanced arthritis, where the cartilage that cushions the knee joint has deteriorated, leading to pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility. Patients often report chronic pain that limits daily activities, along with swelling and a decreased range of motion. Other conditions that may necessitate a knee replacement include post-traumatic arthritis resulting from injury and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder that affects the joint lining.
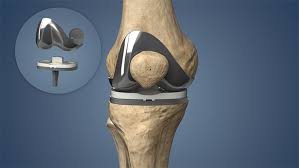
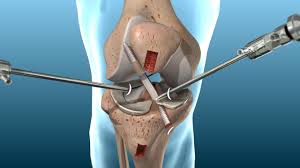
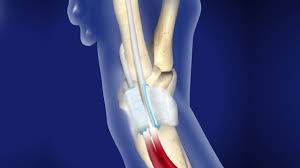
During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision over the knee, exposes the joint, and removes the damaged bone and cartilage. This is followed by the careful placement of metal and plastic components that mimic the natural knee joint. Modern advancements in surgical techniques and prosthetic designs have significantly improved the outcomes of primary knee replacement surgeries, leading to shorter recovery times and higher patient satisfaction rates.
Postoperative care is crucial for successful recovery. Patients typically undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the knee. The rehabilitation process varies for each individual but generally involves a combination of exercises aimed at improving flexibility, strength, and overall function. Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, play an essential role in the recovery process, helping patients achieve a better quality of life.
In summary, primary knee replacement is a highly effective surgical option for individuals suffering from debilitating knee conditions. By replacing the damaged joint with artificial components, this procedure can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility. With appropriate postoperative care and rehabilitation, most patients can return to their daily activities and enjoy a better quality of life following surgery.